|
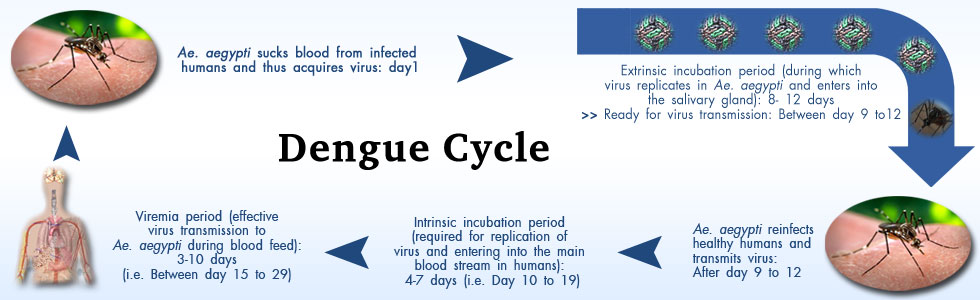
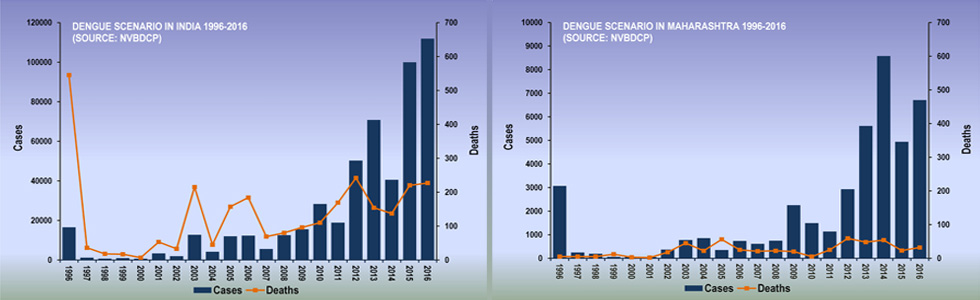
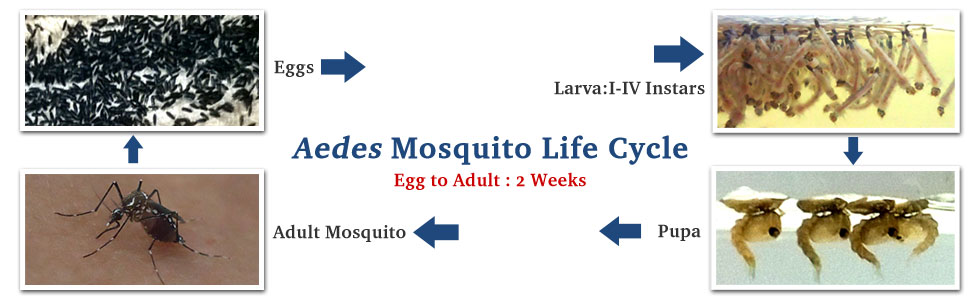
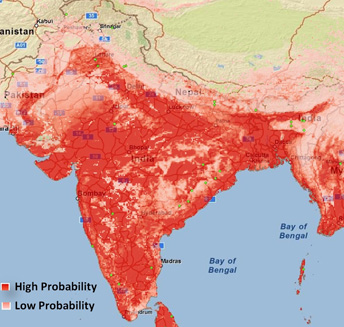
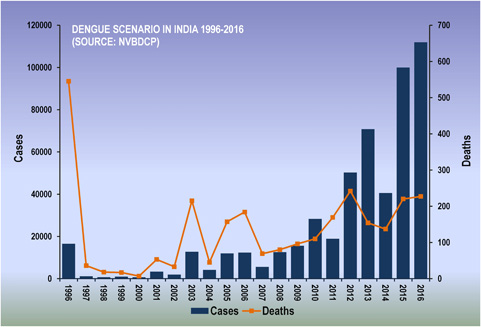
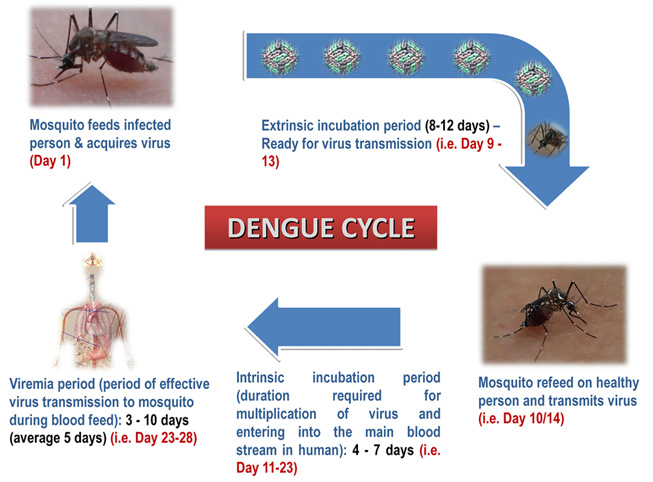
Dengue Disease Dengue disease also known as "breakbone fever" is the most rapidly spreading mosquito-borne viral disease in the world, and is transmitted by the bite of a female mosquito infected with one of the four dengue virus serotypes (DEN-1, DEN-2, DEN-3 and DEN-4). All four serotypes can cause the full spectrum of disease from a subclinical infection to a mild self limiting disease, the dengue fever (DF) and a severe disease that may be fatal, the dengue haemorrhagic fever/dengue shock syndrome(DHF/ DSS). Dengue is a tropical disease, endemic in more than 110 countries with more than one-third of the world's population living in areas at risk for infection and leading cause of illness and death in the tropics and subtropics (http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs117/en/). In India, the first epidemic illness compatible clinically with dengue was recorded in Chennai in 1780 and the first virologically proved epidemic of dengue fever (DF) occurred in Kolkata and Eastern Coast of India in 1963-1964 (Gupta et al., 2012). Dengue is not transmitted from person to person. An infection can occur by a single bite of mosquito infected with dengue virus. As many as 400 million people are infected yearly. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), more than 2.5 billion people live in dengue-endemic areas with about 50 million DENV infections and 500,000 DHF/DSS cases occurring each year.
There is no vaccine or any specific medication to treat dengue and treatment method mainly relies on the symptoms. Main characteristic manifestations of dengue illness are (Source NVBDCP);
|
||||||